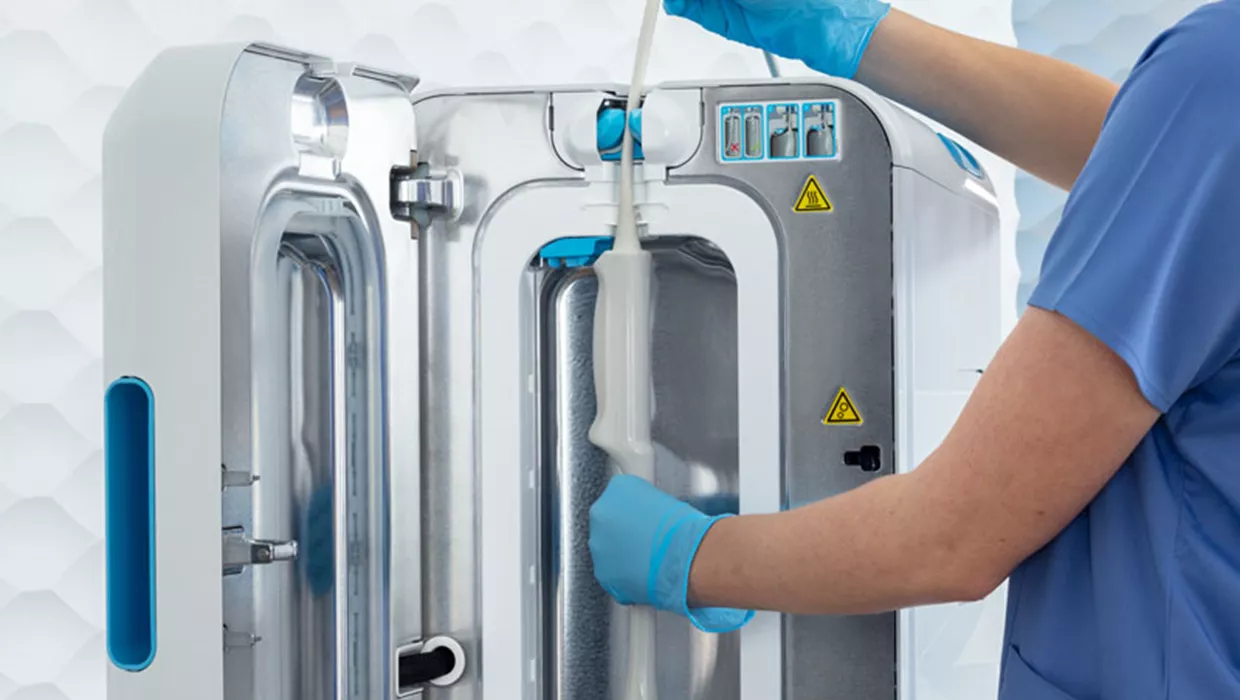
- Ultrasound Probe Reprocessing Solutions
- Ultrasound Probe Reprocessing Solutions
- Introducing
- Infection Prevention - What to Consider?
- Products and Solutions
- Learning and Support
- Learning and Support
- Guidelines and Tools
- Nanosonics Academy
- Endoscope Reprocessing Solutions
- Endoscope Reprocessing Solutions
- Endoscope Reprocessing Solutions
- Endoscope Reprocessing Solutions
- Importance of Reprocessing
- Biofilm
- Problem with manual cleaning
- The next gold standard
- About Us
- About Us
- Contact Us
- Contact Us
- Contact Us
- The Team
- Our Story
- Investor Centre
- The Centre
- Nanosonics Academy
Choose your country and language
You are currently on